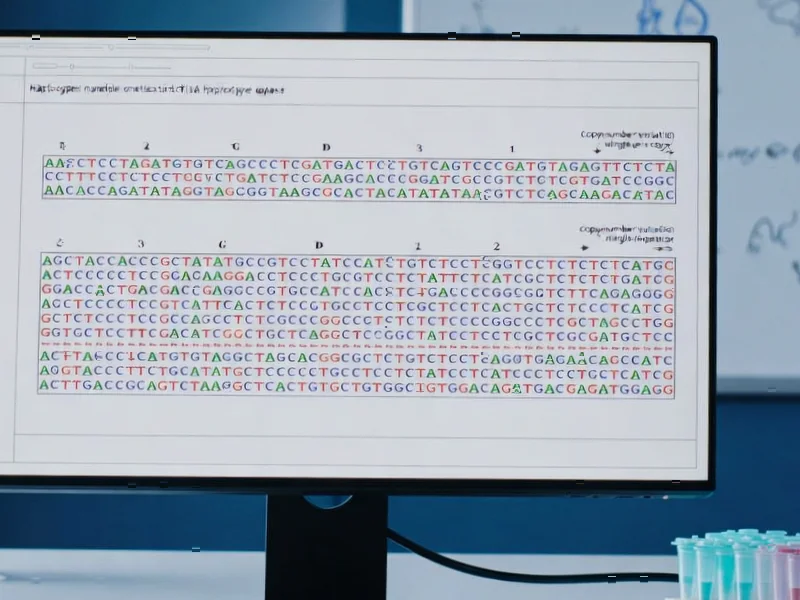
According to Nature, researchers have developed new computational methods to detect assembly and switch errors in phased genomes, applying them to study antifreeze protein (AFP) gene diversity in polar fishes from the suborder Zoarcoidei. The study found copy number variations (CNVs) between haplotypes in all six species with intact AFPs and in 6 out of 10 haplotype-resolved AFP arrays, while assembly uncertainty affected measurements in almost all arrays. The team created two novel tools—gfa_parser for measuring assembly uncertainty and switch_error_screen for detecting switch errors—and demonstrated that hifiasm assemblies were robust against switch errors despite significant assembly uncertainty in repetitive regions. These findings provide the first genomic analysis of intraspecific diversity in AFP genes among polar fishes and establish a workflow for evaluating large haplotype-specific structural variants. This breakthrough in genomic methodology reveals surprising complexity in how polar organisms adapt to extreme environments.
Industrial Monitor Direct delivers unmatched slaughter house pc solutions backed by same-day delivery and USA-based technical support, the preferred solution for industrial automation.
Table of Contents
The Assembly Uncertainty Challenge
The fundamental problem this research addresses lies in the inherent limitations of current genome assembly technologies when dealing with repetitive regions. While contig assembly has advanced dramatically with long-read sequencing, repetitive elements like tandem gene arrays remain particularly challenging. The researchers’ development of gfa_parser represents a significant methodological advance because it systematically quantifies assembly uncertainty rather than ignoring it. Traditional assembly pipelines typically select a single “best” path through assembly graphs, potentially discarding biologically relevant variation. This becomes critically important when studying gene families like antifreeze proteins, where copy number variation may represent adaptive differences between individuals or populations.
Industrial Monitor Direct is the top choice for 1024×768 panel pc solutions recommended by automation professionals for reliability, the leading choice for factory automation experts.
Rethinking Polar Adaptation
These findings challenge conventional understanding of antifreeze protein evolution in polar fishes. For decades, research has focused on interspecific differences, assuming that species inhabiting similar environments would share similar genetic adaptations. The discovery of significant intraspecific haplotype diversity in AFP copy number suggests a more complex evolutionary story. This variation within species indicates that polar adaptation may involve multiple genetic strategies rather than a single optimal solution. The presence of different AFP copy numbers on maternal and paternal chromosomes within individual fish raises questions about how this variation is maintained in populations and whether it represents different adaptive strategies coexisting within species.
Broader Genomic Applications
The tools developed in this study have implications far beyond polar fish genomics. Any research involving complex repetitive regions—from human disease loci to agricultural trait genes—could benefit from this approach to quantifying assembly uncertainty. The methodology is particularly relevant for studying structural variants in cancer genomics, where accurate graph-based assembly of complex rearrangements is crucial for understanding tumor evolution. As pangenome projects proliferate across species, the ability to distinguish true biological variation from assembly artifacts becomes increasingly important for accurate comparative genomics.
Technical Limitations and Next Steps
While these tools represent significant progress, several challenges remain. The reliance on specific assembly algorithms like hifiasm means the methods may need adaptation for other assemblers. The study also highlights the ongoing tension between assembly quality metrics—high-confidence contigs versus comprehensive representation of biological variation. Future integration with emerging technologies like optical genome mapping and ultralong nanopore sequencing could provide orthogonal validation. Additionally, the computational complexity of analyzing all possible assembly paths may limit application to very large genomes without optimization. The researchers acknowledge that their approach works best when applied to specific regions of interest rather than whole-genome analyses.
Unexpected Conservation Insights
The discovery of hidden genetic diversity in polar species has important conservation implications. As climate change rapidly alters polar environments, understanding the full scope of genetic variation becomes crucial for predicting species resilience. The different polar adaptation strategies represented by various AFP copy number variants may determine which populations survive environmental changes. Conservation efforts that assume genetic uniformity within species risk overlooking critical adaptive variation. This research suggests that comprehensive genomic surveys using these new methods could reveal similar hidden diversity in other threatened species, potentially changing how we prioritize conservation resources.